Ferric Maltol vs. Other Oral Iron Therapies: Key Differences and Advantages
Tired of feeling like you’re stuck in a time warp, watching the world zoom by while you’re stuck in the mud? Iron deficiency can leave you feeling sluggish, pale, and generally blah.
We know injectable iron is the express lane to feeling better, a jolt of energy that can have you back to your best in no time. But let’s be honest, who wants to face the needle every time? The thought alone can make you feel drained. And then there are those traditional oral iron pills. They’re like trying to climb a mountain with a backpack full of bricks. Slow, arduous, and often accompanied by an unpleasant symphony of stomach rumbles. You might finally reach the summit, but the journey is anything but enjoyable.
But what if you could have the best of both worlds? Imagine an iron therapy that’s as effective as a rocket launch, delivering a burst of energy that leaves injectable iron in the dust. Yet, instead of a trip to the doctor’s office, you simply pop a pill. This isn’t your grandma’s iron supplement. This is Ferric Maltol.
Ferric Maltol is the bridge between the lightning-fast results of injectables and the effortless convenience of oral therapy. It is the best Oral Iron Therapy for Iron Deficiency Anemia treatment. It’s the iron revolution you’ve been waiting for. Imagine a world where overcoming iron deficiency is as easy as taking your daily vitamins. No more needles, no more stomach discomfort, just pure, potent iron delivered straight to your bloodstream. Buckle up, because this ride is about to get exciting.
Understanding Oral Iron Therapies
Oral iron therapies are the mainstay of treatment for iron deficiency anemia (IDA). Common options include ferrous sulfate, gluconate, fumarate, and iron polysaccharides [1]. These supplements are generally affordable and easy to administer. However, they often suffer from poor absorption, particularly when taken with food or other medications. Additionally, GI side effects like nausea, constipation, and diarrhea are common, leading to poor patient adherence [2]. Ferric Maltol is a newer iron therapy that aims to address these challenges with improved tolerability and bioavailability.
What is Ferric Maltol?
Ferric Maltol is a novel oral iron therapy that combines ferric iron with a maltol ligand. This unique formulation enhances iron stability and solubility, leading to improved absorption in the gut [3]. The maltol component helps protect the iron from degradation and facilitates its uptake by the intestinal cells. Ferric Maltol advantages include:
- Enhanced Tolerability: Significantly lower incidence of GI side effects compared to traditional iron salts [4].
- Improved Bioavailability: Efficient absorption maximizes iron delivery to the body by this highly bioavailable iron supplement [5].
- Ease of Use: Convenient once or twice daily dosing.

Comparing Ferric Maltol with Other Oral Iron Therapies
Bioavailability and Absorption:
Ferrous salts, such as ferrous sulfate, often have poor absorption due to their low solubility and interactions with food and other medications. Ferric Maltol, with its stable molecular structure, exhibits significantly better absorption, ensuring more efficient iron delivery to the body [6].
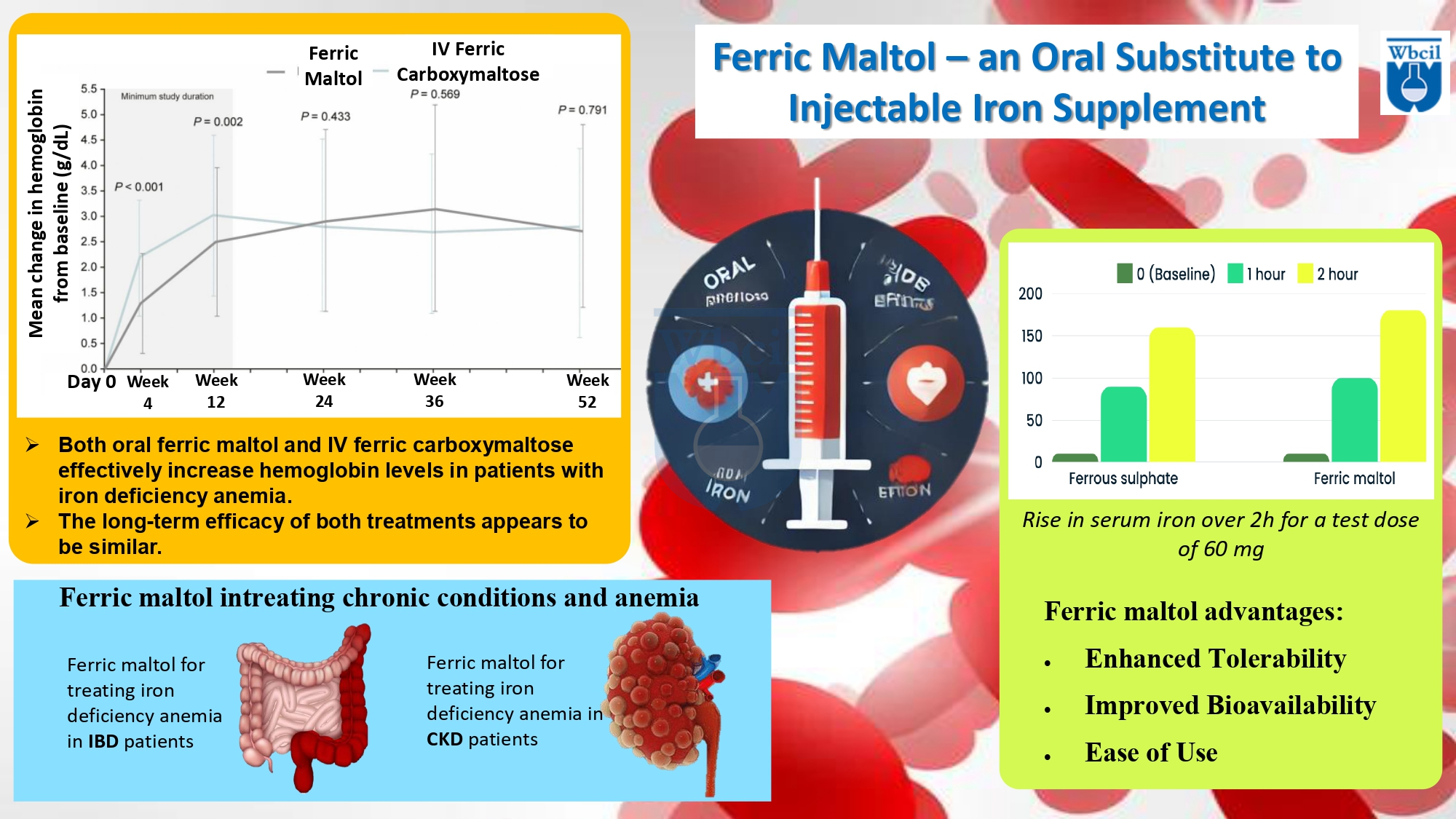
A study shows serum iron levels over 2 hours after a 60 mg dose of iron as either ferrous sulfate (FeSO₄) or ferric maltol. Baseline levels were similar for both forms. FeSO₄ caused a substantial rise at 1 hour, peaking at 160 µmol/L at 2 hours. Ferric maltol showed a greater increase, reaching 180 µmol/L at 2 hours, indicating superior absorption. Both forms demonstrated a time-dependent serum iron rise, with maltol consistently outperforming FeSO₄. These findings suggest ferric maltol may be a more efficient option for raising serum iron levels, which could influence treatment decisions for iron deficiency management [7].
Gastrointestinal Tolerability
- Ferric Maltol Vs. Ferrous Sulfate: Well-known for causing nausea and constipation.
- Ferric Maltol Vs. Ferrous Fumarate: Often leads to bloating and diarrhea.
- Ferric Maltol: Demonstrates a significantly lower incidence of gastrointestinal side effects due to its targeted release mechanism, making it more tolerable for patients.
Dosage and Compliance:
Traditional iron supplements often require high dosages, which can lead to poor patient compliance. Ferric Maltol dosage is lower, that is improves adherence without compromising efficacy.
Efficacy in Treating Iron Deficiency Anemia:
Clinical data has shown Ferric Maltol’s advantages in:
- Raising hemoglobin levels
- Replenishing iron stores effectively
Compared to traditional iron supplements, Ferric Maltol dosage requires shorter treatment durations or lower dosages to achieve similar therapeutic outcomes [8].
Ferric maltol is an oral substitute to injectable iron supplement. The data demonstrates that ferric maltol is an effective oral alternative to injectable iron supplements, such as IV ferric carboxymaltose, for treating iron deficiency anemia. Both treatments achieve comparable hemoglobin responder rates (~75-90%) over time, with no statistically significant differences observed at key time points, including the primary endpoint at Week 12. While IV ferric carboxymaltose may show slightly higher responder rates at certain intervals, ferric maltol provides similar clinical outcomes with the added benefit of being a non-invasive, convenient oral therapy [9]. This makes ferric maltol particularly advantageous for patients requiring long-term iron supplementation, improving treatment adherence and reducing the need for healthcare interventions. Thus, ferric maltol serves as a reliable oral substitute for injectable iron absorption therapy.
Special Applications of Ferric Maltol
Ferric Maltol is particularly well-suited for chronic conditions and anemia:
Treatments for Anemia in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Demonstrated efficacy in managing anemia with minimal GI distress, unlike many ferrous salts [10,11]. Iron deficiency anemia (IDA) is a common complication associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Conventional oral iron supplements are often associated with significant gastrointestinal side effects and may contribute to worsening of the underlying disease. This multicenter Phase 3 clinical trial evaluated the safety and efficacy of ferric maltol, a ferric (Fe) iron complex with maltol (3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4-pyrone), as an innovative oral treatment option for IDA.
Iron Therapies for Chronic Kidney Disease Patients (CKD): Offers a safer and more effective option compared to traditional iron absorption therapies in these patient populations [12]. Ferric maltol is a promising oral iron treatment for chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients with iron deficiency anemia treatment. In a study, patients taking ferric maltol showed significant improvements in hemoglobin levels, iron markers, and overall iron stores compared to those on placebo. The treatment was generally well-tolerated, with only mild gastrointestinal side effects reported in some cases [13]. Ferric maltol offers an effective and convenient alternative to traditional iron therapies for CKD patients.
Cost Considerations
While the initial cost of Ferric Maltol may be slightly higher than traditional iron absorption therapies, its improved tolerability, higher bioavailability, and reduced need for high dosages can offset this difference. Fewer side effects and improved patient compliance can lead to lower healthcare costs in the long run.
Key Advantages of Ferric Maltol
- Superior Tolerability: Ideal for patients who cannot tolerate ferrous salts due to significant GI side effects [14].
- Higher Bioavailability: Ensures faster and more efficient iron replenishment.
- Broad Applicability: Suitable for a wide range of patients, including those with chronic conditions or dietary restrictions.
- Fewer Drug Interactions: Compared to ferrous salts, which can interact with various medications.
Challenges and Limitations of Ferric Maltol
- Slightly higher cost compared to traditional oral iron supplements.
- Limited availability in some regions.
- May require a prescription in certain cases.
Ongoing research is focused on addressing these limitations and expanding the availability of Ferric Maltol [15,16].
WBCIL’s Role in Advancing Iron APIs
West Bengal Chemical Industries Limited (WBCIL) is a leading manufacturer of high-quality iron APIs, including Ferric Maltol, Ferric Carboxymaltose, Ferrous Bisglycinate, and Ferric Ammonium Citrate. WBCIL adheres to stringent GMP-certified manufacturing practices and is committed to developing innovative iron APIs that are effective, eco-friendly, and affordable. WBCIL plays a crucial role in supporting healthcare providers globally with superior iron formulations.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Ferric Maltol offers significant advantages over traditional oral iron therapies, including improved tolerability, higher bioavailability, and broader applicability. Its potential to enhance patient outcomes and improve compliance makes it a valuable option for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia treatment. Healthcare professionals are encouraged to consider Ferric Maltol for their patients, especially those who experience difficulty tolerating ferrous salts.
1. https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB15598
2. Wikipedia contributors. (2025, January 25). Ferric maltol. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia Retrieved 12:00, January 29, 2025, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Ferric_maltol&oldid=1271663759
3. Schmidt C, Allen S, Kopyt N, Pergola P. Iron Replacement Therapy with Oral Ferric Maltol: Review of the Evidence and Expert Opinion. J Clin Med. 2021 Sep 28;10(19):4448. doi: 10.3390/jcm10194448. PMID: 34640466; PMCID: PMC8509126. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8509126/
4. https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/ferric-maltol-oral-route/description/drg-20530913
5. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/drugs/23845-ferric-maltol-capsules
6. https://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-177626/ferric-maltol-oral/details
7. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/ferric-maltol
8. https://ashpublications.org/ashclinicalnews/news/4708/FDA-Approves-Ferric-Maltol-for-Treatment-of-Iron
9. Olsson KM, Fuge J, Brod T, Kamp JC, Schmitto J, Kempf T, Bauersachs J, Hoeper MM. Oral iron supplementation with ferric maltol in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J. 2020 Nov 12;56(5):2000616. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00616-2020. PMID: 32444411; PMCID: PMC7676873. https://publications.ersnet.org/content/erj/56/5/2000616
10. Stallmach A, Büning C. Ferric maltol (ST10): a novel oral iron supplement for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia in inflammatory bowel disease. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2015;16(18):2859-67. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2015.1096929. Epub 2015 Nov 23. PMID: 26595432. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26595432/
11. Christoph Gasche, Tariq Ahmad, Zsolt Tulassay, Daniel C. Baumgart, Bernd Bokemeyer, Carsten Büning, Stefanie Howaldt, Andreas Stallmach, Ferric Maltol Is Effective in Correcting Iron Deficiency Anemia in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Results from a Phase-3 Clinical Trial Program, Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, Volume 21, Issue 3, 1 March 2015, Pages 579–588, https://doi.org/10.1097/MIB.0000000000000314
12. Oral Ferric Maltol for the Treatment of Iron-Deficiency Anemia in Patients With CKD: A Randomized Trial and Open-Label Extension, Pergola, Pablo E. et al., American Journal of Kidney Diseases, Volume 78, Issue 6, 846 – 856.e1. https://www.ajkd.org/article/S0272-6386(21)00624-7/fulltext
13. Pergola PE, Kopyt NP. Oral Ferric Maltol for the Treatment of Iron-Deficiency Anemia in Patients With CKD: A Randomized Trial and Open-Label Extension. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021 Dec;78(6):846-856.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2021.03.020. Epub 2021 May 23. PMID: 34029682. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34029682/
14. Khoury A, Pagan KA, Farland MZ. Ferric Maltol: A New Oral Iron Formulation for the Treatment of Iron Deficiency in Adults. Annals of Pharmacotherapy. 2021;55(2):222-229. doi:10.1177/1060028020941014
15. Cummings JF, Fraser A, Stansfield C, Beales I, Sebastian S, Hoque S. Ferric maltol Real-world Effectiveness Study in Hospital practice (FRESH): clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with inflammatory bowel disease receiving ferric maltol for iron-deficiency anaemia in the UK. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2021 Feb;8(1):e000530. doi: 10.1136/bmjgast-2020-000530. PMID: 33622683; PMCID: PMC7907848. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33622683/
16. https://www.mskcc.org/cancer-care/patient-education/medications/adult/ferric-maltol
