Bisglycinate vs. Melatonin: Magnesium as the Safer Sleep Solution
In the nutraceutical industry, the “sleep vertical” is arguably the most dynamic sector today. As stress levels rise globally, consumers are desperate for rest. For years, the market response has been dominated by one molecule: Melatonin. However, a significant shift is occurring in formulation science. We are moving away from hormonal manipulation and toward physiological support. This shift is placing magnesium for sleep at the center of modern product development.
For brand owners and formulators, the challenge is clear. While Melatonin is effective for resetting the body clock, it does not address the underlying physiological tension that keeps people awake. This is where magnesium for sleep support shines. Specifically, magnesium bisglycinate for sleep is emerging as the superior alternative for long-term use, offering a safety profile that hormones simply cannot match.
Key Takeaways:
Why? Because consumers are moving away from hormonal sedatives like melatonin in favor of safer, long-term solutions that address the root causes of insomnia, such as stress and nutrient deficiency.
Who? For nutraceutical brand owners and formulators seeking a reliable sleep supplement ingredient manufacturer to create non-addictive, premium sleep products that drive customer retention.
What? A shift toward WBCIL’s magnesium APIs, specifically Magnesium Bisglycinate, which offers superior bioavailability and “smart” relaxation compared to generic minerals or hormonal fixes.

Understanding the Mechanism: Melatonin vs Magnesium for Sleep
To understand why magnesium for sleep is often the safer choice, we must look at the biochemistry.
Melatonin is a hormone produced by the pineal gland. Its primary role is circadian rhythm support—it signals to the body that it is time to sleep. It is a “chronobiotic,” meaning it does not necessarily sedate; it shifts timing. This makes it excellent for jet lag or shift work. However, using a hormone nightly to treat stress-induced insomnia can lead to melatonin side effects, such as daytime grogginess, vivid dreams, and potential desensitization of receptors.
In contrast, magnesium for sleep works on a different pathway entirely. Magnesium is a natural NMDA receptor antagonist and a GABA agonist. Simply put, it acts as the “brake” for the body’s nervous system. It facilitates nervous system relaxation by blocking excitatory signals in the brain. It does not force the body to sleep; it creates the biological conditions in which sleep can naturally occur.
The Superiority of Bisglycinate: The “Smart” Magnesium
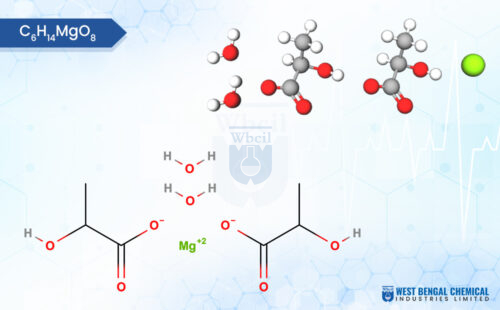
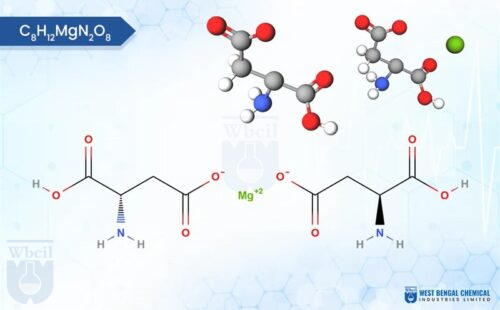
Not all magnesium is created equal. For sleep formulations, magnesium bisglycinate for sleep (often referred to interchangeably as magnesium glycinate for sleep) is the gold standard.
Why? Because it binds magnesium to the amino acid glycine.
- Bioavailability: Inorganic salts like magnesium oxide are poorly absorbed and often cause digestive distress. Bisglycinate is highly stable and passes through the intestinal wall intact, ensuring the magnesium for sleep benefits actually reach the bloodstream.
- The Glycine Effect: Glycine itself acts as an inhibitory neurotransmitter. Furthermore, glycine helps lower core body temperature, a physiological prerequisite for deep sleep. When you use magnesium bisglycinate for sleep, you are getting two sleep aids in one molecule.
Addressing the Root Cause: Nutrient Deficiency and Insomnia
A major reason why magnesium for sleep is so effective is that it addresses a widespread hidden hunger. Estimates suggest that a vast majority of the adult population does not meet the daily dietary requirement for magnesium.
Nutrient deficiency and lack of sleep insomnia are closely connected. Without adequate magnesium, muscles cannot relax, and the stress hormone cortisol remains increased.
By correcting this deficiency, magnesium for sleep supplementation restores the body’s ability to down-regulate at night. Unlike sedatives that mask symptoms, magnesium for sleep resolves the biochemical gap causing the restlessness.
Safety Profile: The Non-Addictive Sleep Supplement
For B2B brands, consumer retention is driven by safety. One of the strongest selling points for magnesium for sleep is that it is a non addictive sleep supplement.
There is no risk of dependency. There is no “rebound insomnia” when a user stops taking it. This stands in sharp contrast to melatonin side effects, where high doses over long periods can potentially disrupt the body’s endogenous production. Magnesium for sleep is a nutrient, not a drug-like intervention. It supports sleep hygiene and supplementation protocols seamlessly, allowing users to wake up feeling refreshed rather than “hungover.”
Stress and Sleep Quality: The Biochemical Link
Modern insomnia is rarely just about a broken clock; it is about a racing mind. This is the intersection of stress and sleep quality.
Magnesium regulates the HPA axis (Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal axis), which controls our stress response. When we are stressed, we waste magnesium. This creates a vicious cycle: stress depletes magnesium, and low magnesium amplifies stress. Magnesium for sleep products break this cycle.
Magnesium sleep benefits extend beyond just falling asleep. Studies suggest that magnesium can improve “sleep efficiency”—the percentage of time spent asleep while in bed—and reduce early morning awakenings. By calming the sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight), magnesium for sleep allows the parasympathetic system (rest and digest) to take over.
Commercial Viability: Choosing the Right Magnesium
For a sleep supplement ingredient manufacturer, the stability and purity of the raw material are paramount.
At West Bengal Chemical Industries Limited (WBCIL), we understand that the efficacy of a final product depends on the quality of the API. WBCIL’s magnesium APIs, particularly our Magnesium Bisglycinate, are engineered for high solubility and palatability.
We provide magnesium for sleep solutions that are:
- Fully Reacted: Ensuring the magnesium is truly bound to glycine, not just a dry blend.
- High Purity: Free from heavy metals and contaminants, manufactured in WHO-GMP certified facilities.
- Formulation Friendly: Suitable for capsules, powders, and functional beverages.
As European and global regulations around hormones like melatonin become stricter, magnesium for sleep represents a future-proof investment for nutraceutical brands.
Conclusion: The Future is Mineral
The era of simply “knocking out” consumers with heavy sedatives is ending. The modern consumer wants health optimization. They want magnesium sleep benefits that improve their overall well-being, not just their night.
While melatonin has its place for circadian disorders, magnesium for sleep—specifically magnesium bisglycinate for sleep—offers a comprehensive, restorative, and safe solution for chronic support. It treats the body, not just the clock.
Yes. Since they work on different pathways—melatonin on circadian rhythm support and magnesium on nervous system relaxation—they can be complementary. However, using magnesium for sleep alone is often sufficient for stress-related insomnia and avoids potential melatonin side effects.
Unlike sleeping pills, magnesium for sleep is a nutrient that builds up in the system. While the relaxation effect of magnesium bisglycinate for sleep can be felt within an hour due to the glycine, full correction of nutrient deficiency and insomnia issues may take a few weeks of consistent use.
Yes, in the industry, these terms are often used interchangeably. Magnesium glycinate for sleep usually refers to magnesium bisglycinate (where one magnesium molecule is attached to two glycine molecules). This specific chelate is preferred for magnesium for sleep products because it is gentle on the stomach.
WBCIL’s magnesium APIs are manufactured under strict WHO GMP guidelines. We focus on creating fully reacted mineral chelates that offer superior stability and bioavailability. This ensures that when a brand claims magnesium sleep benefits, their product actually delivers them.
Our diverse portfolio addresses several high-demand verticals:
Injectable Iron APIs: Including Ferric Carboxymaltose, Iron Isomaltoside, and Ferric Derisomaltose.
Liposomal Nutraceuticals: Advanced delivery systems for Vitamin C, Glutathione, Magnesium, and Iron, designed for superior absorption.
Mineral Chelates: Highly soluble forms like Magnesium Bisglycinate, Ferrous Bisglycinate, and Zinc Gluconate.
Pellets: Sustained-release and enteric-coated pellets for precise dosage formulation.
Fine Chemicals: Reagents and precursors for pharmaceutical synthesis.