-
Product Name:
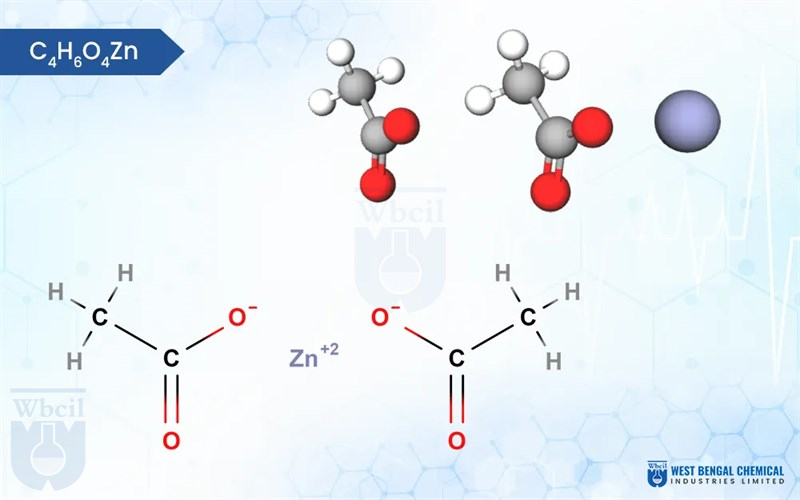
Zinc Acetate
-
Molecular Formula:
C4H6O4Zn · 2H2O
-
Molecular Weight:
219.51 g/mol
-
CAS No.:
5970-45-6
-
CID Code:
11192
-
Shelf Life:
3 years - 20°C powder
-
ATC Code (WHO)
A16AX05
-
DrugBank ID
DB14487
-
ChemSpider ID
10719
-
UNII No.
H2ZEY72PME
- USP
- IUPAC Names
- Synonyms
- MSDS
USP of Zinc Acetate
- Zinc acetate is best known for its potential to reduce the duration and severity of cold symptoms when used as a lozenge and is also used as a dietary supplement to address zinc deficiencies.
- Zinc acetate is used as a food additive, primarily as a flavoring agent. It can enhance the taste and aroma of certain foods and beverages.
IUPAC Names of Zinc Acetate
zinc;diacetate
Synonyms of Zinc Acetate
- Zinc Acetate
- 557-34-6
- Zinc diacetate
- Zinc(II) acetate
- Dicarbomethoxyzinc
- Acetic acid, Zinc salt
- Acetic acid, Zinc(II) salt
MSDS of Zinc Acetate
Download MSDS PDF- MSDS Name: Zinc Acetate Dihydrate
- Product Code: ZAD9600
- Relevant identified uses of the substance or mixture and uses advised against: Laboratory chemicals, Manufacture of substances
- General advice: Consult a physician. Show this safety data sheet to the doctor in attendance.
- If inhaled: If breathed in, move person into fresh air. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. Consult a physician.
- In case of skin contact: Wash off with soap and plenty of water. Consult a physician.
- In case of eye contact: Rinse thoroughly with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes and consult a physician.
- If swallowed: Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Rinse mouth with water. Consult a physician.
- Most important symptoms and effects, both acute and delayed: The most important known symptoms and effects are described in the labelling (see section 2.2) and/or in section 11
- Indication of any immediate medical attention and special treatment needed: No data available
- Suitable extinguishing media: Use water spray, alcohol-resistant foam, dry chemical or carbon dioxide.
- Special hazards arising from the substance or mixture: Carbon oxides, Zinc/zinc oxides
- Advice for firefighters: Wear self-contained breathing apparatus for firefighting if necessary.
- Further information: no data available
- Control parameters: Components with workplace control parameters
- Appropriate engineering controls: Handle in accordance with good industrial hygiene and safety practice. Wash hands before breaks and at the end of workday.
- Eye/face protection: Safety glasses with side-shields conforming to EN166 Use equipment for eye protection tested and approved under appropriate government standards such as NIOSH (US) or EN 166(EU).
- Skin protection: Handle with gloves. Gloves must be inspected prior to use. Use proper glove removal technique (Without touching glove’s outer surface) to avoid skin contact with this product. Dispose of contaminated gloves after use in accordance with applicable laws and good laboratory practices. Wash and dry hands. The selected protective gloves have to satisfy the specifications of EU Directive 89/686/EEC and the standard EN 374 derived from it.
- Body Protection: Complete suit protecting against chemicals, The type of protective equipment must be selected according to the concentration and amount of the dangerous substance at the specific workplace.
- Respiratory protection: For nuisance exposures use type P95 (US) or type P1 (EU EN 143) particle respirator. For higher level protection use type OV/AG/P99 (US) or type ABEK-P2 (EU EN 143) respirator cartridges. Use respirators and components tested and approved under appropriate government standards such as NIOSH (US) or CEN (EU).
- Control of environmental exposure: Prevent further leakage or spillage if safe to do so. Do not let product enter drains. Discharge into the environment must be avoided.
- Appearance Form: Crystalline or Granules
- Color: White
- Odour: Slight acetous Odour
- pH (5% w/v): 6.00 – 8.0
- Melting point/freezing point: 237 °C
- Initial boiling point and boiling range: no data available
- Sublimation Temperature: no data available
- Density: no data available
- Vapour pressure: no data available
- Vapour density: no data available
- Refractive density: 1,840 g/cm3
- Water solubility: Freely soluble in water
- Decomposition temperature: no data available
- Viscosity: no data available
- Other safety information: No data available
- https://whmis.org/sds/
- https://www.osha.gov/sites/default/files/publications/OSHA3514.pdf
- https://reachonline.eu/reach/en/annex-ii.html
- https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Zinc-acetate-dihydrate
- https://echa.europa.eu/da/registration-dossier/-/registered-dossier/17716
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zinc_acetate
Description of Zinc Acetate
Zinc acetate is a versatile chemical compound with interesting properties. Typically found in its dihydrate form (Zn (CH3COO)2·2H2O), it appears as colorless crystals with a white, chalky texture. Interestingly, unlike many salts, zinc acetate is odorless. It exhibits good hydroscopic character, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the air. On the scientific side, zinc acetate dissolves well in water, making it a useful industrial material.
Chemically, it’s a salt formed by the combination of zinc ions (Zn²⁺) and acetate ions (CH3COO⁻). The zinc ion is surrounded by four acetate ions in a tetrahedral arrangement, giving the molecule its overall structure. This unique combination of physical and chemical properties makes zinc acetate valuable in various applications, from dietary supplements to wood preservation.
As a leading API manufacturer, WBCIL prioritizes strict CGMP and ISO quality control measures throughout the production process. The prolonged experience from 1962 ensures consistent potency, purity, and safety in every dose of WBCIL’s zinc acetate.
Application of Zinc Acetate
Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Industry
- Zinc deficiency treatment: It’s used as a dietary supplement to treat and prevent zinc deficiency.
- Immune support: Zinc acetate supplements can help boost immune function, especially in elderly people.
Nutraceutical Industry
- Dietary supplements: Zinc acetate is formulated into tablets, capsules, and lozenges as a highly bioavailable form of zinc 3.
- Cold remedies: Zinc acetate lozenges are used to manage common cold symptoms.