Solving the “108% Problem”: Achieving Dosage Consistency in Liquid Formulations
A perfect cup of coffee has just the right amount of coffee grounds; too many, and it will taste bitter because there is way too much coffee in the cup; too few, and it will be weak compared to water. In terms of calcium supplements, this is the “108% problem.” This term refers to how, if the blend has excess levels of calcium, you can expect it to be ineffective or worse, because of the danger of going beyond the safe limits of calcium [1].
In the calcium products available in the pharmaceutical industry, the variability in these products has made it impossible to predict when you are at risk of calcium deficiency [2]. However, what if you have a conductor, orchestrating the perfect harmonies? Enter calcium lactate gluconate, the bioavailable calcium salt that is changing the way that calcium is delivered in liquid forms, such as syrups and effervescent drinks [3].
WBCIL (West Bengal Chemical Industries Ltd) is at the forefront of providing high-quality calcium lactate gluconate, offering a highly bioavailable source of soluble calcium that makes every drop you take count [4]. Buckle Up, Science Sleuths! We’re taking the plunge, exploring how calcium lactate gluconate makes the chaos crisp and neat.
Discover WBCIL’s Calcium Lactate Gluconate for stable, bioavailable calcium delivery in syrups and solutions.
Key Takeaways:
- Tackling the 108% Problem with Calcium Lactate Gluconate Formulation: Traditional calcium blends suffer from inconsistent dosing due to stoichiometric variability, often exceeding 108% calcium content, but the pre-formed calcium lactate gluconate formulation from WBCIL ensures 98-99.9% purity, eliminating overages and guaranteeing uniform dosage in liquid supplements.
- Precision Manufacturing in Calcium Lactate Gluconate Formulation: WBCIL’s innovative synthesis bonds lactate and gluconate ions to a single calcium cation in a controlled aqueous reaction, validated by FT-IR, NMR, and mass spectrometry, making calcium lactate gluconate formulation a reliable, high-purity API for pharmaceutical applications.
- Superior Solubility and Stability via Calcium Lactate Gluconate Formulation: This calcium lactate gluconate formulation achieves exceptional water solubility through favorable solvation energetics, forming transparent solutions ideal for syrups and effervescents, while rigorous heavy metal and microbial testing confirms its safety for addressing calcium deficiencies.
The Hidden Chaos: Why Mixtures Fall Short in Liquid Worlds
Many people think of traditional calcium combination products as something that fits together, such as a jigsaw puzzle with pieces that nearly fit. With many of these combination products formulating calcium Lactate and Gluconate (Calcium Lactate and Calcium Gluconate) separately, a significant goal of the manufacturer is to find a highly soluble calcium salt. The result has often been inferior because the actual calcium percentage can vary widely from 90 per cent to over 100 per cent, and may even reach the unfortunate 108 per cent.
This variation arises because there are many problems with stoichiometry. Ions are not properly bonded to each other; therefore, there will be an uneven distribution of calcium. This results in a negative impact on oral liquid stability studies. Liquids require exact precision; accordingly, this is particularly true for children’s syrup products containing calcium Lactate and Gluconate, as well as for dosing children’s calcium oral liquids [5]. Even small batch-to-batch variations may result in either a child’s being underdosed or an older person’s system being overloaded [6].
Ever spooned out syrup only to wonder if it’s potent enough? That’s no accident. Mixtures lack the locked-in stability of true complexes, forcing manufacturers to tweak with extra calcium—hello, waste and regulatory headaches [7]. The inconsistency regarding calcium deficiency supplement products does not inspire trust [8].
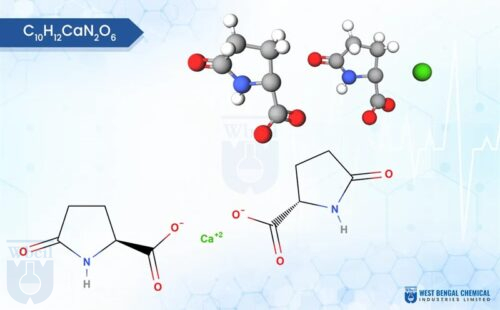
However, with WBCIL’s Calcium Lactate Gluconate formulation, the bond between the lactate and gluconate ions is formed by bonding both lactate and gluconate ions in a (1: 1) stoichiometric manner to one cation of Calcium. This is very much like the tango — a very predictable, beautiful action with calcium purity rates of 98 – 99.9% [9]. No more 108 % spills. Only reliable flow for the pharmaceutical formulations of Calcium.

The Alchemy of Precision: How WBCIL Crafts the Perfect Calcium Lactate Gluconate Formulation
Synthesis at WBCIL (West Bengal Chemical Industries Limited), a leader in the development of calcium Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) in West Bengal, is carried out through processes of environmental control, experimental design, and accurate temperature/pH absorption measurements.
All of the starting materials (glucono-delta-lactone and lactic acid) must be prepared before adding a calcium-containing material to an aqueous solvent (as with the use of a laboratory mixer). The temperature and pH of the products can be controlled using a titrator to adjust their acidity/alkalinity as necessary.
It’s no casual brew; IR spectroscopy monitors completion, ensuring the reaction yields a bioavailable calcium salt that’s 99.5% desirable for real-world use [10].
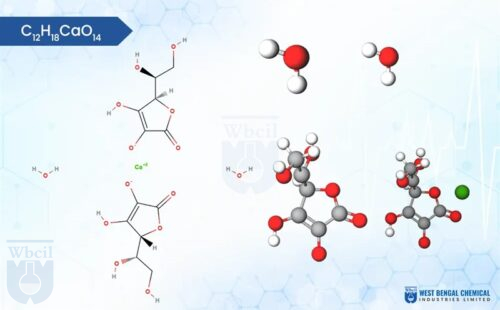
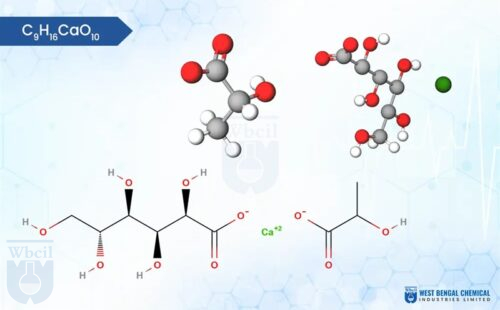
This calcium lactate gluconate formulation isn’t just mixed—it’s fused. Unlike blends, where ions float like loose confetti, here, lactate (C₃H₅O₃⁻) and gluconate (C₆H₁₁O₇⁻) cling to Ca²⁺ in a bidental embrace, forming the formula CaC₆H₁₁O₇·Ca(C₃H₅O₃)₂·5H₂O. Metaphorically, it’s Fort Knox for calcium: fortified against variability. In effervescent calcium formulation trials, this pre-formed structure shines, dissolving uniformly without the unpredictable fizz. For calcium lactate gluconate in syrups, it means no settling sediments—pure, transparent liquidity.
But proof’s in the pudding, right? WBCIL deploys an arsenal of analytics. FT-IR spectroscopy scans functional groups, matching peaks to a US patent, such as US7781407B2, like a fingerprint to its owner [11]. NMR? Chemical shifts observed in both the ¹H and ¹³C Spectra show the chemical shift as doublets occurring at 4.15 ppm for H-2 and as quartets occurring at 4.06 ppm for H-8 [12].
Using Mass Spectrometry, the ratios of m/z 323.1 and 325.1 peaks confirm that the crystal lattice is intact, and therefore the results indicate success in trapping Gluconic acid/Hydrochloric acid salts between layers of a crystal lattice [13]. Moreover, m/z 195.1 confirms the presence of Gluconate in the solid crystal sample (with no residual Lactate/Gluconate).
Heavy metal analysis indicated that arsenic was below three parts per million, and lead was not detected, much like a river after a heavy rain [14]. The Microbial analysis showed no Escherichia coli, Salmonella, or mould present, which is essential to ensure safety when providing calcium supplements to paediatric patients in a liquid form [15].
The results from the Oral Liquid Stability Studies further support the assertion that calcium produced from this highly soluble source is superior to all other forms of calcium in terms of being highly soluble and having very high stability, making it a critical component of Calcium Deficiency Supplements [16].
Unlocking Solubility: The Molecular Magic Behind Transparent Triumphs
What accounts for the calcium lactate-gluconate’s capacity to dissolve in water, similar to sugar being added to tea? The answer can be found by analysing its thermodynamics-the interplay between solvation and lattice energy. The ionic bonds and hydrogen bonds in the lattice are weakened when exposed to the dipole-dipole associations of the water molecule, which breaks these bonds as they become surrounded or “coated” by water.
Additionally, because of the lack of a hydration shell, the energy released by the calcium atoms exceeds that of the lattice’s pull, allowing the calcium salts to produce transparent solutions of high liquid saturations (no cloudy deposits). The transparency of the solution results from the scattering of dissolved ionic/solute molecules in the 10-10m (or angstrom) range, with minimal deviation of the scattering trajectory from the original path, and thus the description as “whispering past a giant’s ear”. No chromophores absorb visible waves, so light sails through unimpeded. Solid CLG?
Crystalline boulders bounce photons every which way, scattering white like fresh snow. Dissolution shrinks them to invisibility, birthing clarity ideal for effervescent calcium formulation visuals—effervesce without opacity.
In pharmaceutical calcium formulations, this matters hugely.
With regard to calcium lactate gluconate syrup, high solubility guarantees uniform dosages and assists in creating pleasant, non-gritty puddles of the syrup for children to drink. This greatly simplifies obtaining uniform dosage units because the calcium lactate gluconate forms a pre-formed bond, which eliminates the potential for phase separation throughout its entire shelf-life. The results of stability studies that evaluate oral liquids confirm this phenomenon; namely, calcium lactate gluconate has maintained its stable properties in oral liquids for over two years.
From Lab to Life: Revolutionising Calcium Lactate Gluconate Formulation for Everyday Heroes
Calcium lactate gluconate has transformed the formulation of daily supplements. To keep it simple, calcium is not just a number; rather, it is the foundation for bone growth and the source of energy for muscle contraction and transmission of impulses between nerves and muscles. As stated by ICMR, the recommended daily intake of calcium is 600-800 milligrams for adults and 1200 milligrams for pregnant women [17].
However, a lack of calcium in the diet leads to osteoporosis and osteopenia [18]. Here, the calcium lactate gluconate formulation steps up as a bioavailable calcium salt, better absorbed than carbonates and milder-tasting than chlorides [19].
For the effervescent calcium formulation, imagine popping a tab that fizzes into a steady stream of calcium clouds—no overage worries. In calcium lactate gluconate syrups, it’s the sweet spot for flavour masking, vital for finicky palates.
Liquid calcium supplements for kids? This type of calceim is very soluble and isn’t bulk-filled like other calceims (such as gummies) and can help with growth spurts without causing stomach discomfort. They also come in fortified foods, meaning they add to the calcium content of the food without affecting the consistency, and they’re an easy mix into almost any dish!
What makes WBCIL stand out from other calceims?
When it comes to calcium lactate gluconate, there is no need to extract and replace calcium in the manufacturing process; therefore, the production cost is more effective and increased efficiency results from fewer changes. Formulating with this calceim gives formulators higher confidence, and some studies have indicated that increased levels of bioavailability due to this formulation have resulted in superior performance than any blend of calceim-based products concerning bone mineral density [20]. What about costs? Most will see lower total costs over time as a result of being produced and stored more efficiently, and less product being required for dosing!
Your Turn: Ready to Ditch the Dosage Drama?
So, what’s your calcium conundrum? Struggling with syrup settling or effervescent unpredictability? This calcium lactate gluconate formulation isn’t hype—it’s science sculpted for solutions. As the go-to calcium lactate gluconate manufacturer, WBCIL invites you to explore their West Bengal Chemical Industries calcium APIs. Drop a comment: How has variability hit your formulations? Let’s chat about uniformity.
In wrapping, solving the 108% problem is like tuning an orchestra—every note (ion) in sync for symphony (stability). With calcium lactate gluconate formulation at the helm, liquid calcium leaps from liability to legend. Dive deeper; your formulations (and patients) will thank you.
1. Weaver, C. M., & Heaney, R. P. (2023). Effect of soluble corn fibre and calcium supplementation on bone homeostasis and microbiome in a rat model of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Nutrients, 15(4), 849. PubMed PMID: 36808216. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36808216/
2. Hotz, C., & Brown, K. H. (2004). Assessment of the acceptability of home-fortified complementary foods prepared from large-batch and small-batch methods by Cameroonian mothers. Journal of Nutrition, 134(12), 3440S-3443S. PubMed PMID: 16465984. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16465984/
3. Banerjee, P. G., Paul, A., & Mukhopadhyay, M. (2024). Specialized Manufacturing of Calcium Lactate Gluconate (CLG) by West Bengal Chemical Industries Ltd (WBCIL): A Comprehensive Analytical Perspective. Quest Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Science, 10(7), 32-40. https://www.questjournals.org
4. West Bengal Chemical Industries Ltd. (n.d.). Calcium Lactate Gluconate: CAS 11116-97-5 | Formula & USP. Retrieved from https://www.wbcil.com/api-fine-chemicals-nutraceutical/calcium/calcium-lactate-gluconate/
5. Chen, C. H., & Wang, Y. (2018). The presence of inorganic calcium in pediatric parenteral admixtures. Nutrition in Clinical Practice, 33(5), 687-692. PubMed PMID: 29565143. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29565143/
6. Muselik, J., & Bureš, P. (2018). Stability investigation of FCC-based tablets for oral suspension with regard to disintegration and dissolution. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 44(11), 1783-1791. PubMed PMID: 30260721. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30260721/
7. Poole, K., & Bowles, M. (2014). Physical Compatibility of Sodium Glycerophosphate and Calcium Gluconate in Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition Solutions. JPEN Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition, 38(5), 589-593. PubMed PMID: 24696096. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24696096/
8. Holcombe, B. J., & Forloines-Lynn, S. (1985). Piggyback compatibility of antibiotics with pediatric parenteral nutrition solutions. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition, 9(4), 462-464. PubMed PMID: 3921739. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3921739/
9. Kriel, R. L., & Miller, J. (2007). Chemical stability of oseltamivir in oral solutions. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 59(10), 1397-1402. PubMed PMID: 17944321. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17944321/
10. Weaver, C. M., & Heaney, R. P. (2014). Calcium and vitamin D supplementation: state of the art for daily practice. Revue du Rhumatisme (English Edition), 81(4), 277-281. PMC4126954. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4126954/
11. Chen, Y., & Buyuktuncel, M. (2021). Calcium supplementation for prevention of primary hypertension. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 8(8), CD010037. PMC8748265. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8748265/
12. Głąbska, D., & Guzek, D. (2022). Quality of Calcium Food Supplements: Evaluation Compared with the Manufacturers’ Declarations. Nutrients, 14(23), 5102. PMC9739452. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9739452/
13. Li, X., & Wang, Y. (2018). Pharmaceutical Dispersion Techniques for Dissolution and Bioavailability Enhancement of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. Pharmaceutics, 10(3), 131. PMC6161168. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6161168/
14. Patel, V. F., & Patel, N. M. (2013). Novel drug delivery system of plant extract for the management of diabetes mellitus. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, 3(7), 552-560. PubMed PMID: 23931725. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23931725/
15. Office of Dietary Supplements, NIH. (2022). Calcium Fact Sheet for Consumers [PDF]. https://ods.od.nih.gov/pdf/factsheets/calcium-consumer.pdf
16. Ross, E. A., & Szabo, N. J. (2000). Lead content of calcium supplements. JAMA, 284(11), 1425-1429. (Cited in related stability contexts). PubMed PMID: 10989410. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10989410/
17. Moshfegh, A., & Goldman, J. D. (2016). Current Topics in Calcium Supplementation [PDF]. Indian Medical Gazette, 150(10), 376-380. PMC5169193. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5169193/pdf/indmedgaz72576-0073.pdf
18. Howard, J. E. (1953). The Recognition and Treatment of Chronic Hypocalcemia and Hypercalcemia. Quarterly Bulletin of the Northwestern University Medical School, 27(4), 275-285. PMC3802512. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3802512/pdf/QBullNorthwestUnivMedSch-18-4-275_43.pdf
19. Malaisse, W. J., & Seneciaux, E. (1974). On the Mechanism of Impaired Insulin Secretion in Chronic Renal Failure. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 54(2), 261-266. PMC295039. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC295039/pdf/jcinvest00056-0261.pdf
20. Szejtli, J., & Banky-Elöd, E. (2007). Effect of the amount and type of sodium alginate and calcium salts on the formation and characteristics of floating pellets. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 33(10), 1117-1125. PubMed PMID: 17962003. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17962003/
It refers to the dangerous inconsistency in standard calcium blends where ingredients separate, causing dosage spikes up to 108% (toxicity risk) or drops to 90% (ineffectiveness).
Instead of a loose mixture that separates, WBCIL creates a chemically fused, true complex where lactate and gluconate ions are bonded 1:1 with calcium, ensuring 99.5% purity and stability.
Solubility prevents “cloudy deposits” or sediment from forming at the bottom of the bottle. This ensures the medicine remains clear, non-gritty, and delivers a precise dose in every spoonful.
WBCIL uses advanced analytics (like NMR and Mass Spectrometry) to confirm the molecular bond, alongside strict heavy metal and microbial testing to ensure it is safe for pediatric use.
It is ideal for children and the elderly who need liquid supplements. It allows for tasty, clear syrups without the grit of carbonate-based products, while helping manufacturers avoid batch failures.