-
Product Name:
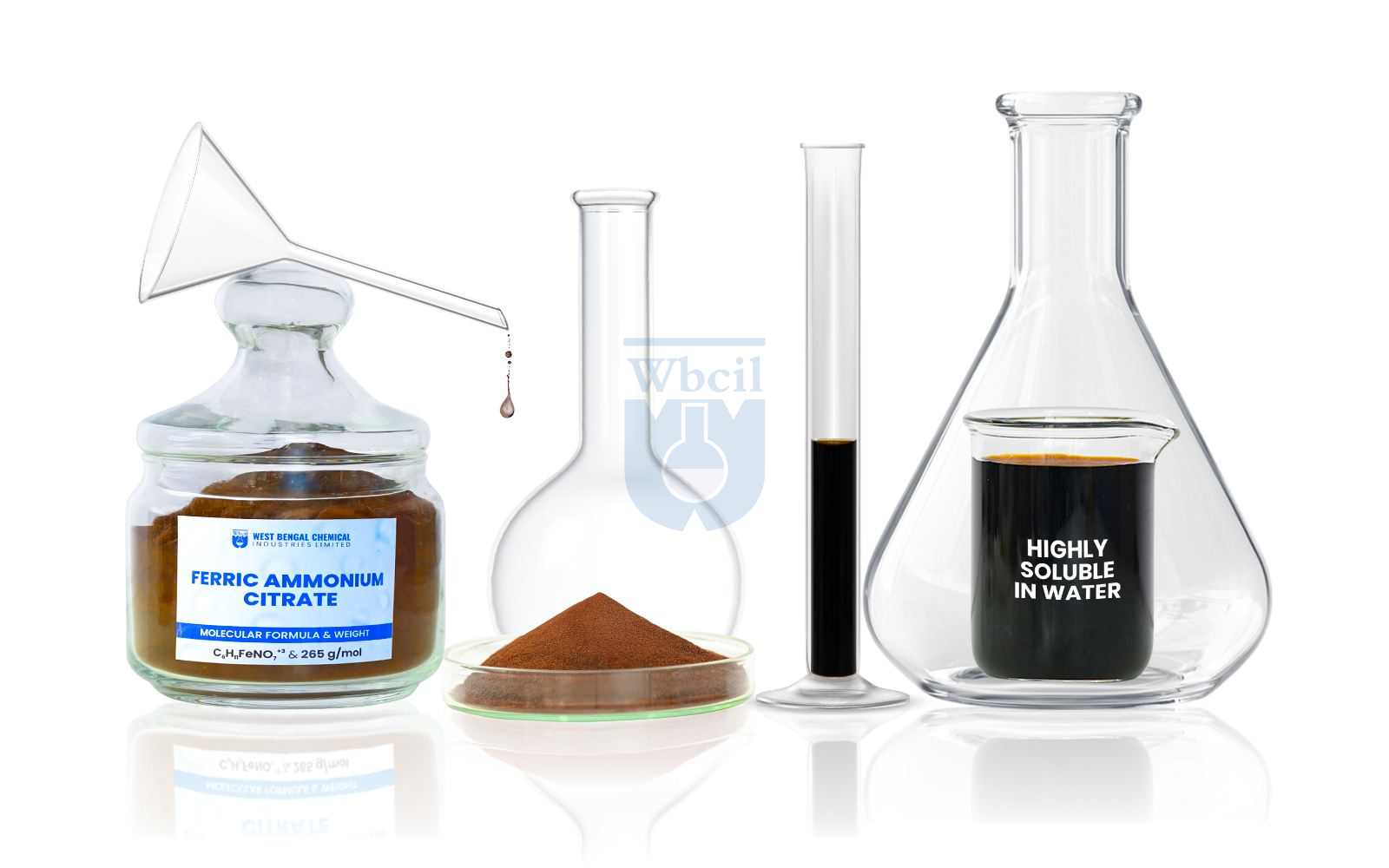
Ferric Ammonium Citrate
-
Molecular Formula:
C6H11FeNO7+3
-
Molecular Weight:
265 g/mol
-
CAS No.:
1185-57-5
-
HSN Code:
29181550
-
CID Code:
14457
-
Shelf Life:
3 years - 20°C powder
-
ATC Code (WHO)
V08CA07 (WHO)
-
DrugBank ID
DB09501
-
ChemSpider ID
8057501
-
UNII No.
UVP74NG1C5
- USP
- IUPAC Names
- Synonyms
- MSDS
USP of Ferric Ammonium Citrate
- Ferric ammonium citrate offers excellent solubility in water, making it easily absorbed by the body. This can be a significant advantage compared to other iron supplements that may have lower absorption rates.
- Unlike some iron supplements, ferric ammonium citrate is known for being gentle on the digestive system and causing minimal stomach upset.
- Ferric ammonium citrate has a wide range of applications, including pharmaceutical formulations, food fortification, and nutritional supplements.
- It is perfectly chelated.
- Can be administered orally or through injection
IUPAC Names of Ferric Ammonium Citrate
azane;2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid;iron(3+)
Synonyms of Ferric Ammonium Citrate
- Iron ammonium citrate
- Ammonium ferric citrate
- Ferric ammonium citrate
- Ferric ammonium citrate, green
- Ammonii ferri citras
- Ammonium iron(3+) citrate
- Iron ammonium citrate, green
- Ferri-ammoniumcitrat, braunes
- Ferric ammonium citrate [USP]
- Ammonium iron(III) citrate
- Iron(III) ammonium citrate
- Citric acid, ammonium iron(3+) salt
- Ferric ammonium citrate,green
- Ammonium Iron (III) Citrate
- Ferric Ammonium Citrate, Brown
- Citric acid, ammonium iron salt, green
- Ammonium iron(3+) 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate
- 1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-, ammonium iron(3+) salt
- 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylic acid ammonium iron (3+) salt
- ammonium iron citrate
- 1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-, ammonium iron(3+) salt
MSDS of Ferric Ammonium Citrate
Download MSDS PDF- MSDS Name: Ferric Ammonium Citrate BP
- Product Code: FACIH20
- GENERAL ADVICE: Consult a physician. Show this safety data sheet to the doctor in attendance.
- IF INHALED: If breathed in, move person into fresh air. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. Consult a physician.
- SKIN CONTACT: Wash off with soap and plenty of water. Consult a physician.
- EYE CONTACT: Rinse thoroughly with plenty of water for 15 minutes and consult a physician.
- IF SWALLOWED: Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Rinse mouth with water. Consult a physician.
- SUITABLE EXTINGUISHING MEDIA: Use water spray, alcohol-resistant foam, dry chemical or carbon dioxide.
- SPECIAL HAZARDS ARISING FROM THE SUBSTANCE OR MIXTURE: Carbon oxides, nitrogen oxides (NOx), Iron oxides.
- ADVICE FOR FIREFIGHTERS: Wear self-contained breathing apparatus for firefighting if necessary.
- FIRE EXTINGUISHING MEDIA: Use fire-extinguishing media appropriate to the surrounding fire.
SMALL FIRE: Use DRY chemical powder.
LARGE FIRE: Use water spray, fog or foam. Do not use water jet. - FURTHER INFORMATION: No data available.
- Personal precautions, protective equipment & emergency procedures: Use personal protective equipment. Avoid dust formation. Avoid breathing vapors, mist or gas. Ensure adequate ventilation. Evacuate personnel to safe areas. Avoid breathing dust.
- Environmental Precautions: Do not let product enter drains.
- Methods and materials for containment & cleaning up: Pick up and arrange disposal without creating dust. Sweep up and keep in suitable, closed containers for disposal.
- Appearance Form: Thin, transparent, dark red scales or granules or brownish red powder. Odorless, deliquescent in moist air, affected by light.
- Color: Brownish red.
- Odour: Odorless
- Solubility: Soluble in 20°C, in 0.5% part of water, almost insoluble in alcohol (95%).
- https://whmis.org/sds/
- https://www.osha.gov/sites/default/files/publications/OSHA3514.pdf
- https://reachonline.eu/reach/en/annex-ii.html
- https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/ferric_ammonium_citrate
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ammonium_ferric_citrate
- https://echa.europa.eu/da/registration-dossier/-/registered-dossier/23100
- https://www.chemicalbook.com/ChemicalProductProperty_EN_CB9729858.htm
Description of Ferric Ammonium Citrate
Ferric ammonium citrate (FAC), also known as ferric ammonium citrate scales or ferric ammonium citrate trihydrate exhibits interesting physical and chemical properties. It is a water-soluble coordination complex with the chemical formula FeC6H5O7(NH4)3•xH2O (where x can vary between 3 and 4). It comes in two forms: a reddish-brown to garnet red and a thin, transparent green, both existing as scales, granules, or powder [1]. Both possess a faint ammonia odor and hygroscopic nature, readily absorbing moisture from the air [1, 2].
The brown form tends to be more granular, while the green form can be scale-like or powdery [2]. Despite the color variation, their chemical composition is similar, containing iron (Fe³⁺), ammonium (NH₄⁺), and citrate (C₆H₅O₇³⁻) ions in a complex structure [2, 3]. The exact formula remains elusive, but it’s generally represented as C₆H₁₁FeNO₇³⁺. The key difference lies in the iron and citric acid content, with the brown form having slightly more iron and the green form boasting a higher citric acid concentration [2, 3].
This intricate interplay between its physical and chemical makeup contributes to FAC’s diverse applications in various fields. As a leading API manufacturer, WBCIL prioritizes strict CGMP and ISO quality control measures throughout the production process. The prolonged experience from 1962 ensures consistent potency, purity, and safety in every dose of WBCIL’s Ferric ammonium citrate.
Ferric Ammonium Citrate has the chemical formula: C6H11FeNO7+3 and molecular weight of ferric ammonium citrate is 265.00 g/mol.
Application of Ferric Ammonium Citrate
Pharmaceutical Industry
Superior Iron Supplements
- Treatment of Anemia: Used in oral iron supplements to treat and prevent iron deficiency anemia.
- Multivitamin Formulations: Included in multivitamin and mineral supplements to provide essential iron.
Medical Imaging
- Contrast Agents: Utilized in some formulations of contrast agents for medical imaging procedures, enhancing image clarity.
- Effective Iron Delivery: Provides a bioavailable form of iron for the body, aiding in the treatment of anemia.
- Versatile Formulation: Easily incorporated into various supplement forms, such as tablets, capsules, and liquid preparations.
Food and Beverage Industry:
Food Fortification
- Fortified Foods: Added to foods such as cereals, flour, and dairy products to enhance their iron content.
- Beverages: Used in the fortification of drinks, including juices and nutritional beverages.
- Nutritional Enhancement: Improves the nutritional profile of food and beverages, helping to address dietary iron deficiencies.
- Wide Acceptance: Generally recognized as safe for use in food products, making it a preferred choice for fortification.
Photography
Cyanotype Printing
- Photographic Processes: Used in the traditional cyanotype printing process to create blueprints and artistic prints.
- High Quality: Produces clear, detailed blueprints and images, valued in artistic and historical photography.
Water Treatment
Water Purification
- Coagulant: Employed as a coagulant in water treatment processes to remove impurities and clarify water.
- Effective Purification: Helps in the efficient removal of contaminants from water, improving water quality.
Agriculture
Plant Nutrition
- Fertilizers: Used in some fertilizers to provide essential iron for plant growth and development.
Benefits of Ferric Ammonium Citrate as Folic Acid
Ferric ammonium citrate combined with folic acid offers significant health benefits, particularly in treating and preventing iron-deficiency anemia. The combination boosts hemoglobin production, addressing both iron and folate deficiencies, which are key for red blood cell formation. This helps improve energy levels, oxygen transport, and reduces fatigue. It’s particularly beneficial for pregnant women, supporting fetal development and preventing neural tube defects. Additionally, it helps in maintaining cognitive function and overall health by replenishing essential nutrients in individuals with poor dietary intake or chronic conditions affecting nutrient absorption.
Ferric Ammonium Citrate (also known as ferric ammonium citrate or ammoniacal ferrous citrate) is a chemical compound that consists of iron (in the ferric, or Fe³⁺, oxidation state) complexed with ammonium and citrate ions. It forms a coordination complex by combining these three components.
Ferric Ammonium Citrate has a range of uses, including:
- As a food ingredient, it serves as an acidity regulator (INS number 381) and is notably used in the Scottish beverage Irn-Bru.
- In water purification processes.
- As a reducing agent for metal salts of low activity, such as gold and silver.
- In medical imaging as a contrast medium.
- As a hematinic (to treat iron deficiency anemia).
Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should consult their healthcare provider before using Ferric Ammonium Citrate. It’s essential to consider individual health conditions and potential risks.
Ferric Ammonium Citrate helps remove impurities from water by forming complexes with contaminants. It aids in coagulation and precipitation, facilitating the removal of suspended particles and organic matter during water treatment processes.
Ferric Ammonium Citrate is generally safe when used according to recommended guidelines. However, individuals with iron overload disorders (hemochromatosis) should avoid its use. Always consult a healthcare professional before taking any medication or supplement.
In microbiology, Ferric Ammonium Citrate is used in Kligler’s Iron Agar (KIA) test to identify enterobacteriaceae bacteria. By observing their metabolism of different sugars, including the production of hydrogen sulfide, this test helps differentiate bacterial species.